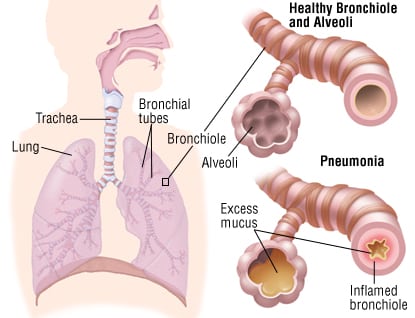
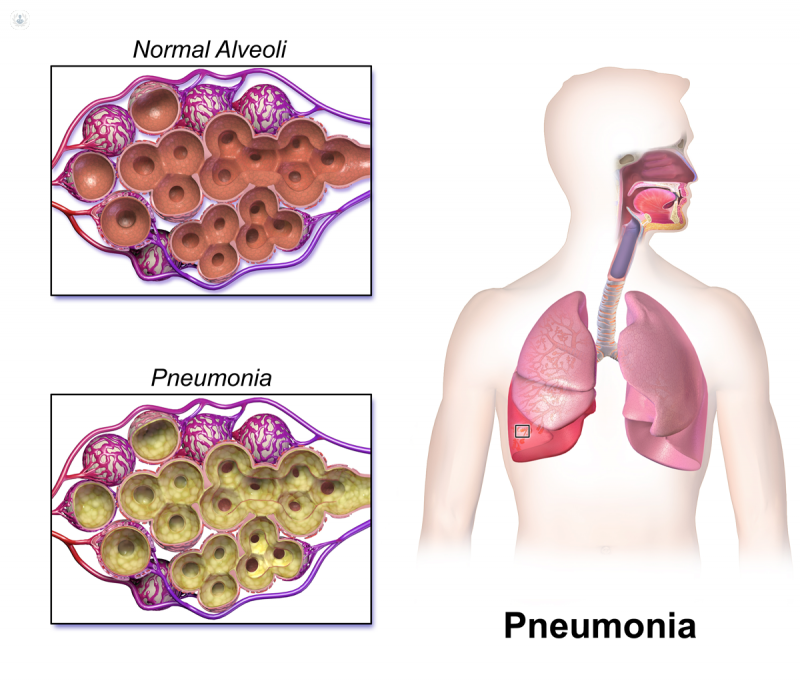
The NHLBI defines pneumonia as a condition that causes difficulty breathing. People who contract this infection are classified according to where they acquired it: community-based, or in the home. Those who are hospitalized have a different type of pneumonia, called hospital-acquired pneumonia. Other types include ventilator-associated pneumonia (HAP), which occurs when people are in the hospital for a prolonged period of time. During the course of a person’s illness, it may be difficult to tell which type of pneumonia is present.
Infants and older adults have a weak immune system and are more likely to contract pneumonia. Those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk for developing this condition. Vaccination is also a good way to prevent the infection from occurring. The treatment for pneumonia depends on the cause of the disease. While proper antibiotic treatment can clear the infection, early discontinuation of the medication may result in a relapse of the infection. In addition, premature stopping of antibiotics may lead to the development of antibiotic resistance, which makes it harder to treat infections.
While the symptoms of pneumonia differ from group to group, some common ones include cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. Babies and infants don’t show any symptoms of the disease. However, adults with a compromised immune system often experience milder symptoms. Older adults who are susceptible to the illness may suffer from sudden changes in mental awareness. Sometimes, bacteria may move from the lung to the bloodstream and cause a condition known as bacterialemia.
The treatment for pneumonia will depend on the type of germs that caused the infection. If it is a virus or bacteria, antibiotics should be used appropriately and without the need for steroids. The symptoms of pneumonia can also vary. Despite its mild symptoms, some older people can even develop septic shock. This can lead to the loss of a loved one’s life. It’s important to get proper medical care as soon as possible.
In cases of pneumonia, symptoms can vary widely. Young children or infants may not show any signs of the infection. Older adults may have more mild symptoms than younger people. Some patients can develop bacterialemia if bacteria are able to move into the bloodstream. If this happens, it can lead to serious complications such as septic shock. Therefore, doctors must carefully evaluate patients to determine their exact conditions and prescribe appropriate treatment. These tests are important and can help your doctor determine the cause of the illness.
The symptoms of pneumonia are different in different age groups. Young children and infants may not show any symptoms at all while adults can exhibit more severe symptoms such as chest pains and fever. In cases where the illness is acute, older adults can suffer from a variety of complications, including bacterialemia, which can lead to septic shock. Acute lung infection can be dangerous for your health and can lead to fatal complications. While the majority of cases of pneumonia will pass without treatment, some people may experience some of the following conditions.
The symptoms of pneumonia will depend on the age of the patient. The symptoms of this condition are mild in newborns and infants, but can be severe in the elderly. In older people, the symptoms of pneumonia can range from fever to sudden changes in mental awareness. Site https://www.dflowcollection.com/
reminds you that it is important to see a doctor immediately if you notice these symptoms or suspect you have pneumonia. Correct diagnosis is the key to your recovery. The sooner you can start treatment, the better.
Your doctor will run a series of tests to diagnose pneumonia. A stethoscope will be used to listen to the patient’s lungs and check for any infections. A chest CT scan will also determine the level of oxygen in the blood. The symptoms of pneumonia vary by age group. In the most severe case, surgery may be required. The infection can be life-threatening if it reaches the heart or brain. For some people, pneumonia is a chronic condition that can take months or years to heal.
The first phase of pneumonia is known as the acute phase. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the lungs, which can cause damage to the fluid and tissues of the airways. The body’s immune system must be protected from infections such as pneumonia. The best treatment will help the patient recover faster. When it comes to the symptoms of the disease, diagnosis can help determine the source of the infection. A patient with this condition may develop a chest infection that causes the chest to expand and lead to other health problems.